Latest News
Star bars show galaxies evolved faster than previously thought
Our astronomers have looked back more than ten billion years in time to find that the Universe’s early galaxies developed much faster than scientists previously thought.
International Masterclass on Particle Physics
On March 22, Durham University's Institute for Particle Physics Phenomenology (IPPP) hosted the International Masterclass on Particle Physics—a hands-on event where high school students analysed real data from the Minerva neutrino detector. Over one hundred students from six local high schools—Durham Johnston, Durham Sixth Form, Newcastle High School for Girls, Thirsk School and Sixth Form, Wellfield Academy, and Sunderland Sixth Form—participated in the event.
Comet 3A and how medieval chroniclers interpreted celestial events
Many people in the UK have been gazing skyward during October, as Comet 3A, dubbed the 'comet of the century' became visible for the first time in 80,000 years. Our scientists scrutinise the cosmos in great detail. But how did medieval chroniclers interpret the skies and their wonders? Giles Gasper from our Department of History and Brian Tanner from our Department of Physics investigate.
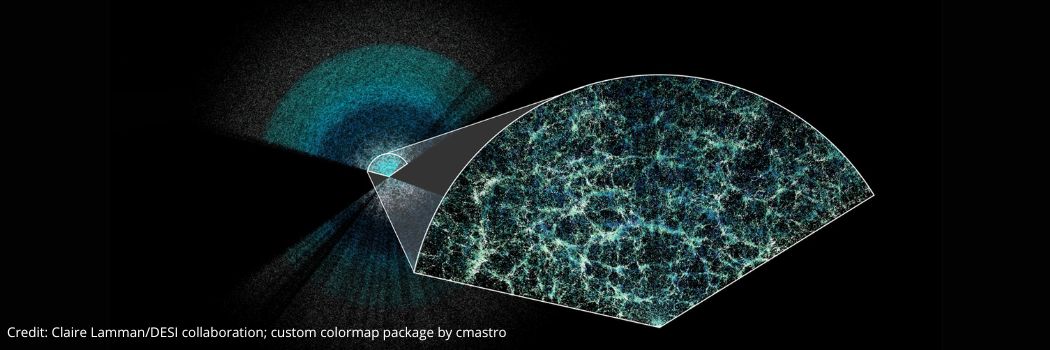
Precisely measuring our expanding Universe
Our physicists are part of an international team that has made the largest 3D map of the Universe, measuring its expansion over 11 billion years.
Durham to power up next generation of fusion scientists and engineers
Researchers in our Physics Department will receive funding for the EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training (CDT) in Fusion Power from the UK’s biggest-ever investment in engineering and physical sciences doctoral skills.
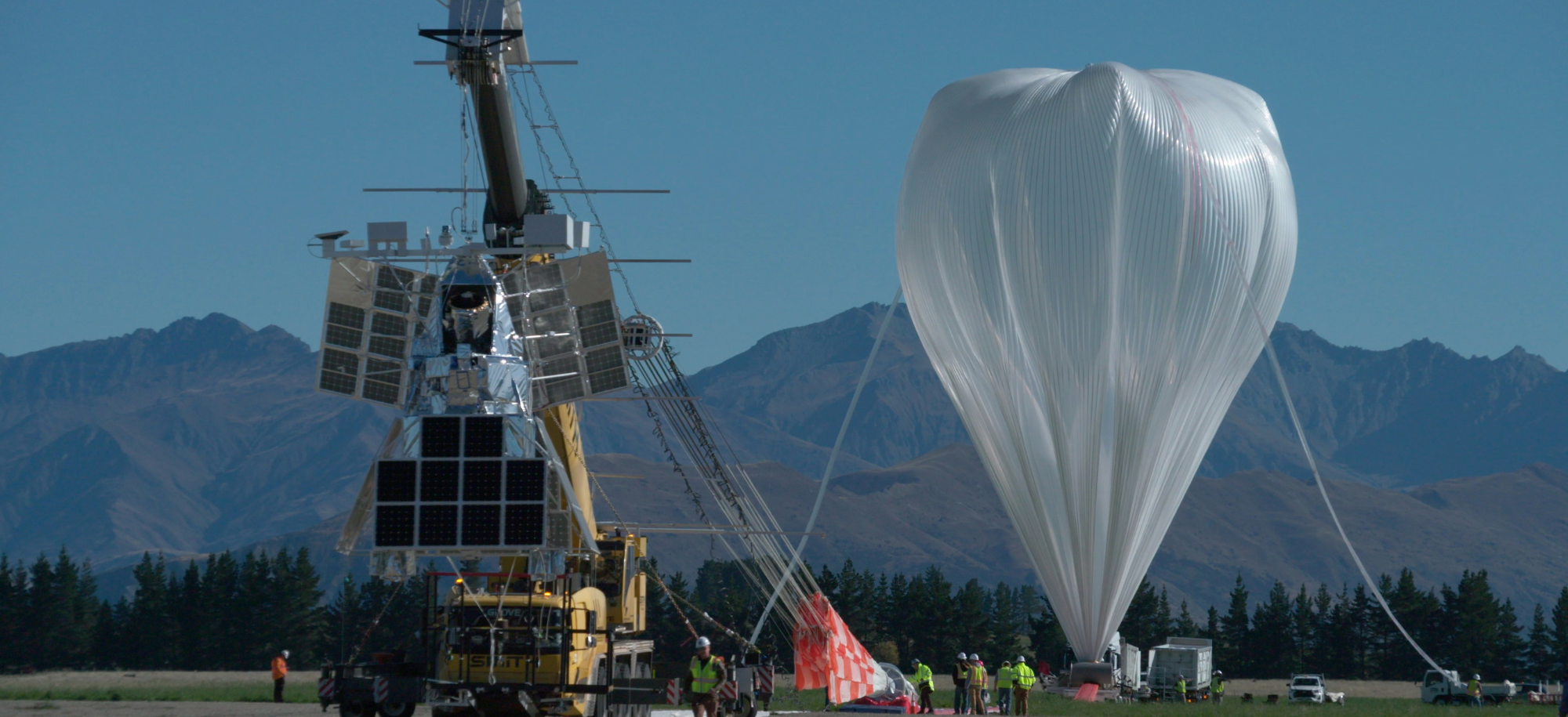
How a balloon-borne experiment can do the job of the Hubble space telescope
Results have shown that balloon-borne experiments to explore space can be just as useful as those launched by rockets, while costing a fraction of the price. Dr Fionagh Thomson and Professor Richard Massey, from our Physics Department, explain how they are also ideal training for the next generation of technology leaders.
Durham Physicists receive funding for EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Fusion Power, making fusion energy commerical and meeting net zero goals
Researchers in the Physics Department at Durham University will receive funding for the EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training (CDT) in Fusion Power from the UK’s biggest-ever investment in engineering and physical sciences doctoral skills.
SuperBIT makes Nature Astronomy front cover
An international project involving Durham University which flew a gigantic balloon-borne telescope to the edge of space has made the front cover of the prestigious journal Nature Astronomy.
Physics Department Developing Talent Awards: 2023-2024 Winners
The Physics Developing Talent Awards scheme was established in 2021 to promote and enhance the careers of early career researchers within the Physics Department. Each year, early career researchers can apply for up to £10,000 to fund a project that will allow them to develop research independence. The scheme is coordinated by the Research Staff Consultative Committee (RSCC).
New research opens avenues for more efficient and stable blue OLED displays
Researchers in our top-rated Physics department are world-leading experts in their field.
In a surprising discovery, our scientists have found that certain molecules long considered poor emitters are actually ideal for boosting efficiency and stability in next-generation blue OLED displays.
The study published in the journal Nature Photonics, reveal an overlooked molecular ‘blind spot’ that could enable major advances in energy-saving display technologies.
New research opens avenues for more efficient and stable blue OLED displays
Researchers in our top-rated Physics department are world-leading experts in their field.
AI-VISION project secures Innovate UK funding to advance precision medicine
A collaborative project between Durham, The Institute of Cancer Research (ICR), The Royal Marsden Hospital, and techbio company Concr, has been awarded a prestigious Innovate UK grant.
The AI-VISION project, which will play a pivotal role in advancing precision (genetically tailored) medicine, has secured a grant of £1million.


/prod01/prodbucket01/media/durham-university/departments-/physics/teaching-labs/VT2A9034-1998X733.jpeg)

.jpg)