Staff profile

| Affiliation |
|---|
| Associate Professor in the Department of Biosciences |
Biography
BSc: 1993 University of Athens, Greece
PhD: 1996 Ludwig-Maximilians University Munich, Germany
Postdoctoral fellow: 1997-2002 University of Chicago, USA
Group leader: 2002-2007 University of Cologne, Germany
Senior Lecturer: 2007-present University of Durham, UK
Dr Karakesisoglou started his academic career at the University of Athens (Greece), where he studied Biology. His PhD thesis conducted under the supervision of Prof. Michael Schleicher (LMU-Munich, Germany) aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms that underpin cellular movement in D. discoideum. Inspired by the power of genetics in addressing fundamental cell biological questions he continued to pursue his goal of elucidating the cytoskeleton in epithelia using relevant mouse models in Prof. Elaine Fuch’s laboratory at the University of Chicago (USA). As a group leader at the University of Cologne (Germany) he pioneered a novel field in cell biology, by studying the functions of a novel complex that spans the mammalian nuclear envelope termed LINC (LInker of the Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton), which functionally integrates the cytoplasmic compartment with the nuclear interior in eukaryotic cells. In 2007 he joined the University of Durham as a senior lecturer. His long-term research interests are to unravel the molecular mechanisms that underpin skin ageing and ageing-associated diseases. Members of his laboratory examine the roles of LINC complex (e.g. nesprins, spectraplakins and SUN-domain proteins) constituents in tissue formation, tissue homeostasis, breast cancer metastasis and motor neuron degeneration.
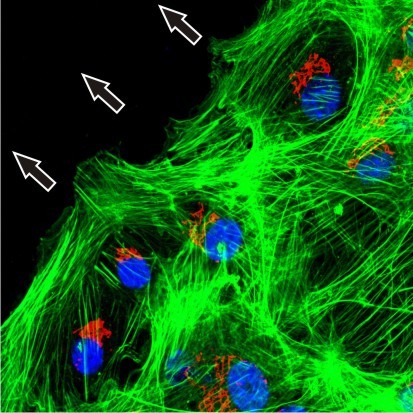
Figure legend: Cell polarization of wild type keratinocytes that are LINC complex positive. Golgi (red), F-actin (green) and nuclei (blue). Note that the majority of cells orient their Golgi apparatus towards the wound edge. Arrows indicate the direction of cell movement.
Research Interests
- Structure and Function of the Nuclear Envelope
- The Role of the Cytoskeleton in Cell Architecture
- The Role of LINC Complex Proteins in Breast Cancer Metastasis
- The Role of LINC Complex Proteins in Motor Neuron Degeneration
- Premature and Physiological Human Ageing
- Skin Biology and Ageing
- Tissue and Animal Morphogenesis
- Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Engineering
Publications
Chapter in book
- Functional Analysis of LINC Complexes in the SkinKarakesisoglou, I., Mroß, C., & Noegel, A. A. (2018). Functional Analysis of LINC Complexes in the Skin. In G. G. Gundersen & H. J. Worman (Eds.), The LINC Complex: Methods and Protocols (pp. 295-306). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8691-0_20
- Detection of Diverse and High Molecular Weight Nesprin-1 and Nesprin-2 Isoforms Using Western BlottingCarthew, J., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2016). Detection of Diverse and High Molecular Weight Nesprin-1 and Nesprin-2 Isoforms Using Western Blotting. In The Nuclear Envelope (pp. 221-232). Humana New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3530-7_14
Journal Article
- Inhibition of PDIs Downregulates Core LINC Complex Proteins, Promoting the Invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells in Confined Spaces In VitroYoung, N., Gui, Z., Mustafa, S., Papa, K., Jessop, E., Ruddell, E., Bevington, L., Quinlan, R. A., Benham, A. M., Goldberg, M. W., Obara, B., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2024). Inhibition of PDIs Downregulates Core LINC Complex Proteins, Promoting the Invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells in Confined Spaces In Vitro. Cells, 13(11), Article 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110906
- An Intronic Heterozygous SYNE2 Splice Site Mutation: A Rare Cause for Myalgia and hyperCKemia?Paulus, T., Young, N., Jessop, E., Berwanger, C., Clemen, C. S., Schröder, R., Ploski, R., Hagel, C., Hellenbroich, Y., Moser, A., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2024). An Intronic Heterozygous SYNE2 Splice Site Mutation: A Rare Cause for Myalgia and hyperCKemia?. Muscles, 3(1), 100-109. https://doi.org/10.3390/muscles3010010
- SIRT2 Inhibition by AGK2 Promotes Perinuclear Cytoskeletal Organisation and Reduces Invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells in Confined In Vitro ModelsJessop, E., Young, N., Garcia-Del-Valle, B., Crusher, J. T., Obara, B., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2024). SIRT2 Inhibition by AGK2 Promotes Perinuclear Cytoskeletal Organisation and Reduces Invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells in Confined In Vitro Models. Cells, 13(23), Article 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232023
- Quantitative morphometric analysis of intrinsic and extrinsic skin ageing in individuals with Fitzpatrick skin types II–IIICostello, L., Goncalves, K., De Los Santos Gomez, P., Simpson, A., Maltman, V., Ritchie, P., Tasseff, R., Isfort, R., Dicolandrea, T., Wei, X., Määttä, A., Karakesisoglou, I., Markiewicz, E., Bascom, C. C., & Przyborski, S. (2023). Quantitative morphometric analysis of intrinsic and extrinsic skin ageing in individuals with Fitzpatrick skin types II–III. Experimental Dermatology, 32(5), 620-631. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.14754
- Biallelic SYNE2 Missense Mutations Leading to Nesprin-2 Giant Hypo-Expression Are Associated with Intellectual Disability and AutismYoung, N., Asif, M., Jackson, M., Fernández-Mayoralas, D. M., de la Peña, M. J., Calleja-Pérez, B., Álvarez, S., Hunter-Featherstone, E., Noegel, A. A., Höhne, W., Nürnberg, P., Obara, B., Hussain, M. S., Karakesisoglou, I., & Fernández-Jaén, A. (2021). Biallelic SYNE2 Missense Mutations Leading to Nesprin-2 Giant Hypo-Expression Are Associated with Intellectual Disability and Autism. Genes, 12(9), Article 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091294
- Culturing Keratinocytes on Biomimetic Substrates Facilitates Improved Epidermal Assembly In VitroHunter-Featherstone, E., Young, N., Chamberlain, K., Cubillas, P., Hulette, B., Wei, X., Tiesman, J. P., Bascom, C. C., Benham, A. M., Goldberg, M. W., Saretzki, G., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2021). Culturing Keratinocytes on Biomimetic Substrates Facilitates Improved Epidermal Assembly In Vitro. Cells, 10(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051177
- Bioengineering the Microanatomy of Human SkinRoger, M., Fullard, N., Costello, L., Bradbury, S., Markiewicz, E., O’Reilly, S., Darling, N., Ritchie, P., Määttä, A., Karakesisoglou, I., Nelson, G., von Zglinicki, T., Dicolandrea, T., Isfort, R., Bascom, C., & Przyborski, S. (2019). Bioengineering the Microanatomy of Human Skin. Journal of Anatomy, 234(4), 438-455. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.12942
- p63 transcription factor regulates nuclear shape and expression of nuclear envelope-associated genes in epidermal keratinocytesRapisarda, V., Malashchuk, I., Asamaowei, I. E., Poterlowicz, K., Fessing, M. Y., Sharov, A. A., Karakesisoglou, I., Botchkarev, V. A., & Mardaryev, A. (2017). p63 transcription factor regulates nuclear shape and expression of nuclear envelope-associated genes in epidermal keratinocytes. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 137(10), 2157-2167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2017.05.013
- Nesprins in health and disease.Cartwright, S., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2014). Nesprins in health and disease. Seminars in Cell and Developmental Biology, 29, 169-179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.12.010
- Nesprin interchain associations control nuclear size.Lu, W., Schneider, M., Neumann, S., Jaeger, V., Taranum, S., Munck, M., Cartwright, S., Richardson, C., Carthew, J., Noh, K., Goldberg, M., Noegel, A., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2012). Nesprin interchain associations control nuclear size. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 69(20), 3493-3509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1034-1
- Cytotoxic T lymphocyte effector function is independent of nucleus–centrosome dissociationLui-Roberts, W., Stinchcombe, J., Ritter, A., Akhmanova, A., Karakesisoglou, I., & Griffiths, G. (2012). Cytotoxic T lymphocyte effector function is independent of nucleus–centrosome dissociation. European Journal of Immunology, 42(8), 2132-2141. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201242525
- Cytoskeletal interactions at the nuclear envelope mediated by NesprinsTaranum, S., Sur, I., Muller, R., Lu, W., Rashmi, R., Munch, M., Neumann, S., Karakesisoglou, I., & Noegel, A. (2012). Cytoskeletal interactions at the nuclear envelope mediated by Nesprins. International Journal of Cell Biology, 2012, Article 736524. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/736524
- Roles for nuclear envelope associated Nesprin-2 Giant in cell differentiation, proliferation and chromatin association in a mouse model.Rashmi, R., Eckes, B., Glöckner, G., Groth, M., Muller, R., Munck, M., Neumann, S., Gloy, J., Sellin, L., Walz, G., Schneider, M., Karakesisoglou, I., Eichinger, L., & Noegel, A. (2012). Roles for nuclear envelope associated Nesprin-2 Giant in cell differentiation, proliferation and chromatin association in a mouse model. Nucleus, 3(2), 172-186.
- LINC complex alterations in DMD and EDMD/CMT fibroblasts.Taranum, S., Vaylann, E., Meinke, P., Abraham, S., Yang, L., Neumann, S., Karakesisoglou, I., Wehnert, M., & Noegel, A. (2012). LINC complex alterations in DMD and EDMD/CMT fibroblasts. European Journal of Cell Biology, 91(8), 614-628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2012.03.003
- Molecular mechanisms of centrosome and cytoskeleton anchorage at the nuclear envelope.Schneider, M., Lu, W., Neumann, S., Brachner, A., Gotzmann, J., Noegel, A., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2011). Molecular mechanisms of centrosome and cytoskeleton anchorage at the nuclear envelope. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 68(9), 1593-1610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0535-z
- Nesprin-2 interacts with α-Catenin and regulates Wnt signaling at the nuclear envelope.Neumann, S., Schneider, M., Daugherty, R., Gottardi, C., Eming, S., Beijer, A., Noegel, A., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2010). Nesprin-2 interacts with α-Catenin and regulates Wnt signaling at the nuclear envelope. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(45), 34932-34938. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m110.119651
- Induction of a massive endoplasmic reticulum and perinuclear space expansion by expression of lamin B receptor mutants and the related sterol reductases TM7SF2 and DHCR7.Zwerger, M., Kolb, T., Richter, K., Karakesisoglou, I., & Herrmann, H. (2010). Induction of a massive endoplasmic reticulum and perinuclear space expansion by expression of lamin B receptor mutants and the related sterol reductases TM7SF2 and DHCR7. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 21(2), 354-368. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0739
- The LINC-less granulocyte nucleusOlins, A., Hoang, T., Zwerger, M., Herrmann, H., Zentgraf, H., Noegel, A., Karakesisoglou, I., Hodzic, D., & Olins, D. (2009). The LINC-less granulocyte nucleus. European Journal of Cell Biology, 88(4), 203-14.
- Nesprin-2 Giant (NUANCE) maintains nuclear envelope architecture and composition in skinLuke, Y., Zaim, H., Karakesisoglou, I., Jaeger, V., Sellin, L., Lu, W., Schneider, M., Neumann, S., Beijer, A., Munck, M., Padmakumar, V., Gloy, J., Walz, G., & Noegel, A. (2008). Nesprin-2 Giant (NUANCE) maintains nuclear envelope architecture and composition in skin. Journal of Cell Science, 121(11), 1887-1898. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.019075
- Sun1 forms immobile macromolecular assemblies at the nuclear envelopeLu, W., Gotzmann, J., Sironi, L., Jaeger, V., Schneider, M., Luke, Y., Uhlen, M., Szigyarto, C., Brachner, A., Ellenberg, J., Foisner, R., Noegel, A., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2008). Sun1 forms immobile macromolecular assemblies at the nuclear envelope. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1783(12), 2415-26.
- Delta6-desaturase (FADS2) deficiency unveils the role of omega3- and omega6-polyunsaturated fatty acidsStoffel, W., Holz, B., Jenke, B., Binczek, E., Gunter, R., Kiss, C., Karakesisoglou, I., Thevis, M., Weber, A., Arnhold, S., & Addicks, K. (2008). Delta6-desaturase (FADS2) deficiency unveils the role of omega3- and omega6-polyunsaturated fatty acids. EMBO Journal, 27(17), 2281-2292. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.156
- KASH-domain proteins and the cytoskeletal landscapes of the nuclear envelopeSchneider, M., Noegel, A., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2008). KASH-domain proteins and the cytoskeletal landscapes of the nuclear envelope. Biochem Soc Trans, 36(Pt 6), 1368-72.
- Nesprin-2 giant safeguards nuclear envelope architecture in LMNA S143F progeria cellsKandert, S., Luke, Y., Kleinhenz, T., Neumann, S., Lu, W., Jaeger, V., Munck, M., Wehnert, M., Muller, C., Zhou, Z., Noegel, A., Dabauvalle, M., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2007). Nesprin-2 giant safeguards nuclear envelope architecture in LMNA S143F progeria cells. Human Molecular Genetics, 16(23), 2944-2959. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm255
- CAP2, cyclase-associated protein 2, is a dual compartment proteinPeche, V., Shekar, S., Leichter, M., Korte, H., Schroder, R., Schleicher, M., Holak, T., Clemen, C., Ramanath, Y., Pfitzer, G., Karakesisoglou, I., & Noegel, A. (2007). CAP2, cyclase-associated protein 2, is a dual compartment protein. Cell Mol Life Sci, 64(19-20), 2702-15.
- The inner nuclear membrane protein Sun1 mediates the anchorage of Nesprin-2 to the nuclear envelopePadmakumar, V., Libotte, T., Lu, W., Zaim, H., Abraham, S., Noegel, A., Gotzmann, J., Foisner, R., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2005). The inner nuclear membrane protein Sun1 mediates the anchorage of Nesprin-2 to the nuclear envelope. Journal of Cell Science, 118(15), 3419-3430. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02471
- Lamin A/C-dependent localization of Nesprin-2, a giant scaffolder at the nuclear envelopeLibotte, T., Zaim, H., Abraham, S., Padmakumar, V., Schneider, M., Lu, W., Munck, M., Hutchison, C., Wehnert, M., Fahrenkrog, B., Sauder, U., Aebi, U., Noegel, A., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2005). Lamin A/C-dependent localization of Nesprin-2, a giant scaffolder at the nuclear envelope. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 16(7), 3411-3424. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e04-11-1009
- Enaptin, a giant actin-binding protein, is an element of the nuclear membrane and the actin cytoskeletonPadmakumar, V., Abraham, S., Braune, S., Noegel, A., Tunggal, B., Karakesisoglou, I., & Korenbaum, E. (2004). Enaptin, a giant actin-binding protein, is an element of the nuclear membrane and the actin cytoskeleton. Exp Cell Res, 295(2), 330-9.
- ACF7: An essential integrator of microtubule dynamicsKodama, A., Karakesisoglou, I., Wong, E., Vaezi, A., & Fuchs, E. (2003). ACF7: An essential integrator of microtubule dynamics. Cell, 115(3), 343-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674%2803%2900813-4
- Bridging cytoskeletal intersections.Fuchs, E., & Karakesisoglou, I. (2001). Bridging cytoskeletal intersections. Genes and Development, 15(1), 1-14.
- An epidermal plakin that integrates actin and microtubule networks at cellular junctions.Karakesisoglou, I., Yang, Y., & Fuchs, E. (2000). An epidermal plakin that integrates actin and microtubule networks at cellular junctions. Journal of Cell Biology, 149(1), 195-208.
- Dissection of functional domains by expression of point-mutated profilins in Dictyostelium mutants.Lee, S., Karakesisoglou, I., Noegel, A., Rieger, D., & Schleicher, M. (2000). Dissection of functional domains by expression of point-mutated profilins in Dictyostelium mutants. European Journal of Cell Biology, 79(2), 92-103. https://doi.org/10.1078/s0171-9335%2804%2970011-4
- Identification of a suppressor of the Dictyostelium profilin-minus phenotype as a CD36/LIMP-II homologue.Karakesisoglou, I., Janssen, K., Eichinger, L., Noegel, A., & Schleicher, M. (1999). Identification of a suppressor of the Dictyostelium profilin-minus phenotype as a CD36/LIMP-II homologue. Journal of Cell Biology, 145(1), 167-181.
- Plant profilins rescue the aberrant phenotype of profilin-deficient Dictyostelium cells.Karakesisoglou, I., Schleicher, M., Gibbon, B., & Staiger, C. (1996). Plant profilins rescue the aberrant phenotype of profilin-deficient Dictyostelium cells. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton, 34(1), 36-47. https://doi.org/10.1002/%28sici%291097-0169%281996%2934%3A1%3C36%3A%3Aaid-cm4%3E3.0.co%3B2-g
- Identification of a cyclase-associated protein (CAP) homologue in Dictyostelium discoideum and characterization of its interaction with actinGottwald, U., Brokamp, R., Karakesisoglou, I., Schleicher, M., & Noegel, A. (1996). Identification of a cyclase-associated protein (CAP) homologue in Dictyostelium discoideum and characterization of its interaction with actin. Mol Biol Cell, 7(2), 261-72.
- Structure/function studies on cytoskeletal proteins in Dictyostelium amoebae as a paradigmSchleicher, M., Andre, B., Andreoli, C., Eichinger, L., Haugwitz, M., Hofmann, A., Karakesisoglou, J., Stockelhuber, M., & Noegel, A. (1995). Structure/function studies on cytoskeletal proteins in Dictyostelium amoebae as a paradigm. FEBS Lett, 369(1), 38-42.
- Dictyostelium amoebae that lack G-actin-sequestering profilins show defects in F-actin content, cytokinesis, and developmentHaugwitz, M., Noegel, A., Karakesisoglou, J., & Schleicher, M. (1994). Dictyostelium amoebae that lack G-actin-sequestering profilins show defects in F-actin content, cytokinesis, and development. Cell, 79(2), 303-14.

