Staff profile

| Affiliation | Telephone |
|---|---|
| Professor in the Department of Biosciences | +44 (0) 191 33 41263 |
| Professor in the Biophysical Sciences Institute | |
| Biophysical Sciences Institute Executive Board in the Biophysical Sciences Institute |
Biography
Research Interests
Post-translational Modifications (PTMs) create distinct proteoforms (protein variants) and modulate almost every biological process. This is particularly evident in multicellular organisms where development requires the integration of signals controlling and coordinating cell fates with the environment. Through the development of new biochemical and computational tools my laboratory aims to understanding how Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) peptide modification in plants enable plants to adapt to a changing environment. Recently my laboratory has led the development of the first Cell Atlas of an entire PTM system in any eukaryote. The SUMO cell atlas is an enabling community resource containing novel cell biological, biochemical and genetic tools that allows users to uncover the rules governing how SUMO-dependent signalling is encoded, received, enacted and reset in multicellular organisms. Given the conservation of SUMO across eukaryotes the SUMO Cell Atlas in Arabidopsis could act as a blueprint not just for SUMO systems in other eukaryotes but also for other PTMs. Understanding protein modifications can enable us to develop new strategies for boosting crop prodcutivity under environmental stress.
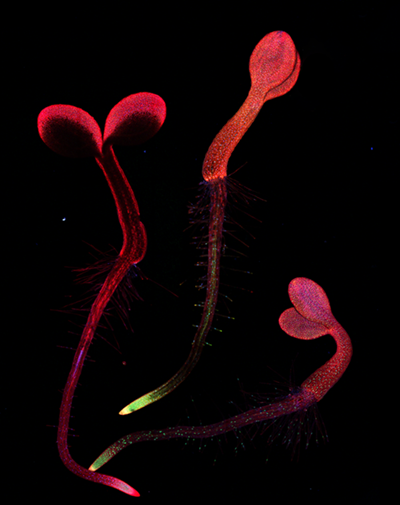
Lab Members:
Dr Cunjin Zhang
Dr. Srayan Ghosh
Dr. Dipan Roy
Dr. Shraboni Ghosh
Dr. Prakash Bhagat
PhD students:
Lisa Clark
Xian Long
Publications
Journal Article
- Elucidating tissue and subcellular specificity of the entire SUMO network reveals how stress responses are fine-tuned in a eukaryoteBanda, J., Ghosh, S., Roy, D., Ingole, K. D., Clark, L., Sharma, E., Kakkunath, S., Sue-Ob, K., Bhosale, R., Band, L., Ghosh, S., Wells, D., Atkinson, J., Provart, N. J., Bennett, M. J., Lilley, K. S., Jones, A., De Lucas, M., Bishopp, A., & Sadanandom, A. (2025). Elucidating tissue and subcellular specificity of the entire SUMO network reveals how stress responses are fine-tuned in a eukaryote. Science Advances, 11(35), Article eadw9153. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adw9153
- Redox-regulated Aux/IAA multimerization modulates auxin responses.Roy, D., Mehra, P., Clark, L., Mukkawar, V., Bellande, K., Martin-Arevalillo, R., Ghosh, S., Ingole, K. D., Bhagat, P. K., Brown, A., Sue-Ob, K., Jones, A., Vermeer, J. E. M., Vernoux, T., Lilley, K., Mullineaux, P., Bechtold, U., Bennett, M. J., & Sadanandom, A. (2025). Redox-regulated Aux/IAA multimerization modulates auxin responses. Science, 389(6757), Article eadu1470. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adu1470
- Redox-regulated Aux/IAA multimerization modulates auxin responsesRoy, D., Mehra, P., Clark, L., Mukkawar, V., Bellande, K., Martin-Arevalillo, R., Ghosh, S., Ingole, K. D., Bhagat, P. K., Brown, A., Sue-Ob, K., Jones, A., Vermeer, J. E., Vernoux, T., Lilley, K., Mullineaux, P., Bechtold, U., Bennett, M. J., & Sadanandom, A. (2025). Redox-regulated Aux/IAA multimerization modulates auxin responses. Science, 389(6757), Article eadu1470. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adu1470
- Recent advances in proteomic workflows to interrogate the SUMOylome in plantsIngole, K. D., Alekseeva, E., Lilley, K. S., & Sadanandom, A. (2025). Recent advances in proteomic workflows to interrogate the SUMOylome in plants. New Phytologist, 247(1), 90-96. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.70176
- POLARIS is a copper-binding peptide that interacts with ETR1 to negatively regulate ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis.Mudge, A. J., Mehdi, S., Michaels, W., Orosa-Puente, B., Shen, W., Tomlinson, C., Wei, W., Hoppen, C., Uzun, B., Roy, D., Hetherington, F. M., Topping, J. F., Sadanandom, A., Groth, G., Robinson, N. J., & Lindsey, K. (2025). POLARIS is a copper-binding peptide that interacts with ETR1 to negatively regulate ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Communications, 101432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2025.101432
- Single-cell transcriptomics reveal how root tissues adapt to soil stressZhu, M., Hsu, C. W., Peralta Ogorek, L. L., Taylor, I. W., La Cavera, S., Oliveira, D. M., Verma, L., Mehra, P., Mijar, M., Sadanandom, A., Perez-Cota, F., Boerjan, W., Nolan, T. M., Bennett, M. J., Benfey, P. N., & Pandey, B. K. (2025). Single-cell transcriptomics reveal how root tissues adapt to soil stress. Nature, 642, 721–729. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08941-z
- Focus on proteolysis.Eckardt, N. A., Genschik, P., Jiang, L., Li, X., Otegui, M. S., Sadanandom, A., Spoel, S., van Wijk, K. J., & Weijers, D. (2024). Focus on proteolysis. The Plant Cell, 36(9), 2929–2930. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae182
- Charting the evolutionary path of the SUMO modification system in plants reveals molecular hardwiring of development to stress adaptationGhosh, S., Mellado Sanchez, M., Sue-Ob, K., Roy, D., Jones, A., Blazquez, M. A., & Sadanandom, A. (2024). Charting the evolutionary path of the SUMO modification system in plants reveals molecular hardwiring of development to stress adaptation. The Plant Cell, 36(9), 3131-3144. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae192
- Inheritance of Resistance to Chickpea Fusarium Wilt Disease ( Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceris Race 2) in a Wide-Cross Cicer arietinum × Cicer reticulatum Mapping FamilyLakmes, A., Jhar, A., Sadanandom, A., Brennan, A. C., & Kahriman, A. (2024). Inheritance of Resistance to Chickpea Fusarium Wilt Disease ( Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceris Race 2) in a Wide-Cross Cicer arietinum × Cicer reticulatum Mapping Family. Genes, 15(6), Article 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060819
- SUMO protease FUG1, histone reader AL3 and chromodomain protein LHP1 are integral to repeat expansion-induced gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana.Sureshkumar, S., Bandaranayake, C., Lv, J., Dent, C. I., Bhagat, P. K., Mukherjee, S., Sarwade, R., Atri, C., York, H. M., Tamizhselvan, P., Shamaya, N., Folini, G., Bergey, B. G., Yadav, A. S., Kumar, S., Grummisch, O. S., Saini, P., Yadav, R. K., Arumugam, S., … Balasubramanian, S. (2024). SUMO protease FUG1, histone reader AL3 and chromodomain protein LHP1 are integral to repeat expansion-induced gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature Plants, 10, 749-759. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-024-01672-5
- SUMOylation of OsPSTOL1 is essential for regulating phosphate starvation responses in rice and ArabidopsisMukkawar, V., Roy, D., Sue-ob, K., Jones, A., Zhang, C., Kumar Bhagat, P., Kakkunnath, S. M., Heuer, S., & Sadanandom, A. (2024). SUMOylation of OsPSTOL1 is essential for regulating phosphate starvation responses in rice and Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 15, Article 1274610. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1274610
- SUMO/deSUMOylation of the BRI1 brassinosteroid receptor modulates plant growth responses to temperatureNaranjo-Arcos, M., Srivastava, M., Deligne, F., Bhagat, P. K., Mansi, M., Sadanandom, A., & Vert, G. (2023). SUMO/deSUMOylation of the BRI1 brassinosteroid receptor modulates plant growth responses to temperature. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 120(4), Article 2217255120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2217255120
- Understanding SUMO-mediated adaptive responses in plants to improve crop productivityClark, L., Sue-Ob, K., Mukkawar, V., Jones, A., & Sadanandom, A. (2022). Understanding SUMO-mediated adaptive responses in plants to improve crop productivity. Essays in Biochemistry, 66(2), 155-168. https://doi.org/10.1042/ebc20210068
- The conjugation of SUMO to the transcription factor MYC2 functions in blue light-mediated seedling development in ArabidopsisSrivastava, M., Srivastava, A. K., Roy, D., Mansi, M., Gough, C., Bhagat, P. K., Zhang, C., & Sadanandom, A. (2022). The conjugation of SUMO to the transcription factor MYC2 functions in blue light-mediated seedling development in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 34(8), 2892-2906. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac142
- TaWRKY10 transcription factor is a novel Jasmonic Acid signalling regulator involved in immunity against Septoria tritici blotch disease in wheatCampanaro, A., Srivastava, A., Zhang, C., Lee, J., Millyard, L., Gatehouse, A., Byrne, E., & Sadanandom, A. (2021). TaWRKY10 transcription factor is a novel Jasmonic Acid signalling regulator involved in immunity against Septoria tritici blotch disease in wheat. Plant Pathology, 70(6), 1397-1408. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13388
- SUMO enables substrate selectivity by mitogen-activated protein kinases to regulate immunity in plantsVerma, V., Srivastava, A. K., Gough, C., Campanaro, A., Srivastava, M., Morrell, R., Joyce, J., Bailey, M., Zhang, C., Krysan, P. J., & Sadanandom, A. (2021). SUMO enables substrate selectivity by mitogen-activated protein kinases to regulate immunity in plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(10), Article e2021351118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2021351118
- SUMO mediated regulation of transcription factors as a mechanism for transducing environmental cues into cellular signaling in plantsRoy, D., & Sadanandom, A. (2021). SUMO mediated regulation of transcription factors as a mechanism for transducing environmental cues into cellular signaling in plants. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 78(6), 2641-2664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03723-4
- HEARTBREAK Controls Post-translational Modification of INDEHISCENT to Regulate Fruit Morphology in CapsellaDong, Y., Majda, M., Šimura, J., Horvath, R., Srivastava, A. K., Łangowski, Ł., Eldridge, T., Stacey, N., Slotte, T., Sadanandom, A., Ljung, K., Smith, R. S., & Østergaard, L. (2020). HEARTBREAK Controls Post-translational Modification of INDEHISCENT to Regulate Fruit Morphology in Capsella. Current Biology, 30(19), 3880-3888.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.07.055
- SUMO Conjugation to BZR1 Enables Brassinosteroid Signaling to Integrate Environmental Cues to Shape Plant GrowthSrivastava, M., Srivastava, A. K., Orosa-Puente, B., Campanaro, A., Zhang, C., & Sadanandom, A. (2020). SUMO Conjugation to BZR1 Enables Brassinosteroid Signaling to Integrate Environmental Cues to Shape Plant Growth. Current Biology, 30(8), 1423.e3-1423.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.01.089
- Towards understanding the multifaceted role of SUMOylation in plant growth and developmentSrivastava, M., Sadanandom, A., & Srivastava, A. K. (2020). Towards understanding the multifaceted role of SUMOylation in plant growth and development. Physiologia Plantarum, 171(1), 77-85. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13204
- Identification of Transgene-Free CRISPR-Edited Plants of Rice, Tomato, and Arabidopsis by Monitoring DsRED Fluorescence in Dry SeedsAliaga-Franco, N., Zhang, C., Presa, S., Srivastava, A. K., Granell, A., Alabadí, D., Sadanandom, A., Blázquez, M. A., & Minguet, E. G. (2019). Identification of Transgene-Free CRISPR-Edited Plants of Rice, Tomato, and Arabidopsis by Monitoring DsRED Fluorescence in Dry Seeds. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, Article 1150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01150
- Dealing With Stress: A Review of Plant SUMO ProteasesMorrell, R., & Sadanandom, A. (2019). Dealing With Stress: A Review of Plant SUMO Proteases. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, Article 1122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01122
- Root branching toward water involves posttranslational modification of transcription factor ARF7Orosa-Puente, B., Leftley, N., von Wangenheim, D., Banda, J., Srivastava, A. K., Hill, K., Truskina, J., Bhosale, R., Morris, E., Srivastava, M., Kümpers, B., Goh, T., Fukaki, H., Vermeer, J. E., Vernoux, T., Dinneny, J. R., French, A. P., Bishopp, A., Sadanandom, A., & Bennett, M. J. (2018). Root branching toward water involves posttranslational modification of transcription factor ARF7. Science, 362(6421), 1407-1410. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau3956
- SUMO conjugation to the pattern recognition receptor FLS2 triggers intracellular signalling in plant innate immunityOrosa, B., Yates, G., Verma, V., Srivastava, A. K., Srivastava, M., Campanaro, A., De Vega, D., Fernandes, A., Zhang, C., Lee, J., Bennett, M. J., & Sadanandom, A. (2018). SUMO conjugation to the pattern recognition receptor FLS2 triggers intracellular signalling in plant innate immunity. Nature Communications, 9(1), Article 5185. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07696-8
- SUMO Suppresses the Activity of the Jasmonic Acid Receptor CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1Srivastava, A. K., Orosa, B., Singh, P., Cummins, I., Walsh, C., Zhang, C., Grant, M., Roberts, M. R., Anand, G. S., Fitches, E., & Sadanandom, A. (2018). SUMO Suppresses the Activity of the Jasmonic Acid Receptor CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1. Plant Cell, 30(9), 2099-2115. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00036
- Revised nomenclature and functional overview of the ULP gene family of plant deSUMOylating proteasesCastro, P. H., Bachmair, A., Bejarano, E. R., Coupland, G., Lois, L. M., Sadanandom, A., van den Burg, H. A., Vierstra, R. D., & Azevedo, H. (2018). Revised nomenclature and functional overview of the ULP gene family of plant deSUMOylating proteases. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69(19), 4505-4509. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery301
- Post-translational modifications in priming the plant immune system: ripe for exploitation?De Vega, D., Newton, A. C., & Sadanandom, A. (2018). Post-translational modifications in priming the plant immune system: ripe for exploitation? FEBS Letters, 592(12), 1929-1936. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13076
- Fifty shades of SUMO: its role in immunity and at the fulcrum of the growth-defence balanceVerma, V., Croley, F., & Sadanandom, A. (2018). Fifty shades of SUMO: its role in immunity and at the fulcrum of the growth-defence balance. Molecular Plant Pathology, 19(6), 1537-1544. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12625
- BTB-BACK Domain Protein POB1 Suppresses Immune Cell Death by Targeting Ubiquitin E3 ligase PUB17 for DegradationOrosa, B., He, Q., Mesmar, J., Gilroy, E. M., McLellan, H., Yang, C., Craig, A., Bailey, M., Zhang, C., Moore, J. D., Boevink, P. C., Tian, Z., Birch, P. R., & Sadanandom, A. (2017). BTB-BACK Domain Protein POB1 Suppresses Immune Cell Death by Targeting Ubiquitin E3 ligase PUB17 for Degradation. PLoS Genetics, 13(1), Article e1006540. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006540
- Stability of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) proteases OVERLY TOLERANT TO SALT1 and -2 modulates salicylic acid signalling and SUMO1/2 conjugation in Arabidopsis thalianaBailey, M., Srivastava, A., Conti, L., Nelis, S., Zhang, C., Florance, H., Love, A., Milner, J., Napier, R., Grant, M., & Sadanandom, A. (2016). Stability of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) proteases OVERLY TOLERANT TO SALT1 and -2 modulates salicylic acid signalling and SUMO1/2 conjugation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67(1), 353-363. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv468
- SUMOylation of phytochrome-B negatively regulates light-induced signaling in Arabidopsis thalianaSadanandom, A., Ádám, É., Orosa, B., Viczián, A., Klose, C., Zhang, C., Josse, E., Kozma-Bognár, L., & Nagy, F. (2015). SUMOylation of phytochrome-B negatively regulates light-induced signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(35), 11108-11113. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1415260112
- Structure and Mechanism of Dimer-Monomer Transition of a Plant Poly(A)-Binding Protein upon RNA Interaction: Insights into Its Poly(A) Tail AssemblyDomingues, M., Sforça, M., Soprano, A., Lee, J., Campos Brasil de Souza, T. de A., Cassago, A., Portugal, R., de Mattos Zeri, A., Murakami, M., Sadanandom, A., de Oliveira, P., & Benedetti, C. (2015). Structure and Mechanism of Dimer-Monomer Transition of a Plant Poly(A)-Binding Protein upon RNA Interaction: Insights into Its Poly(A) Tail Assembly. Journal of Molecular Biology, 427(15), 2491-2506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2015.05.017
- U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase PUB17 acts in the nucleus to promote specific immune pathways triggered by Phytophthora infestansHe, Q., McLellan, H., Boevink, P., Sadanandom, A., Xie, C., Birch, P., & Tian, Z. (2015). U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase PUB17 acts in the nucleus to promote specific immune pathways triggered by Phytophthora infestans. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66(11), 3189-3199. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv128
- Destabilization of interaction between cytokinin signaling intermediates AHP1 and ARR4 modulates Arabidopsis developmentVerma, V., Sivaraman, J., Srivastava, A., Sadanandom, A., & Kumar, P. (2015). Destabilization of interaction between cytokinin signaling intermediates AHP1 and ARR4 modulates Arabidopsis development. New Phytologist, 206(2), 726-737. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13297
- Functional analysis of a Wheat Homeodomain protein, TaR1, reveals that host chromatin remodelling influences the dynamics of the switch to necrotrophic growth in the phytopathogenic fungus Zymoseptoria triticiLee, J., Orosa, B., Millyard, L., Edwards, M., Kanyuka, K., Gatehouse, A., Rudd, J., Hammond-Kosack, K., Pain, N., & Sadanandom, A. (2015). Functional analysis of a Wheat Homeodomain protein, TaR1, reveals that host chromatin remodelling influences the dynamics of the switch to necrotrophic growth in the phytopathogenic fungus Zymoseptoria tritici. New Phytologist, 206(2), 598-605. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13323
- A functional Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) interacting motif (SIM) in the gibberellin hormone receptor GID1 is conserved in cereal crops and disrupting this motif does not abolish hormone dependency of the DELLA-GID1 interactionNelis, S., Conti, L., Zhang, C., & Sadanandom, A. (2015). A functional Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) interacting motif (SIM) in the gibberellin hormone receptor GID1 is conserved in cereal crops and disrupting this motif does not abolish hormone dependency of the DELLA-GID1 interaction. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 10(2). https://doi.org/10.4161/15592324.2014.987528
- Ubiquitin chain topology in plant cell signaling: a new facet to an evergreen storyWalsh, C., & Sadanandom, A. (2014). Ubiquitin chain topology in plant cell signaling: a new facet to an evergreen story. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00122
- Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier protein SUMO enables plants to control growth independently of the phytohormone gibberellinConti, L., Nelis, S., Zhang, C., Woodcock, A., Swarup, R., Galbiati, M., Tonelli, C., Napier, R., Hedden, P., Bennett, M., & Sadanandom, A. (2014). Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier protein SUMO enables plants to control growth independently of the phytohormone gibberellin. Developmental Cell, 28(1), 102-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2013.12.004
- Identification of the domains of cauliflower mosaic virus protein P6 responsible for suppression of RNA silencing and salicylic acid signallingLaird, J., McInally, C., Carr, C., Doddiah, S., Yates, G., Chrysanthou, E., Khattab, A., Love, A., Geri, C., Sadanandom, A., Smith, B., Kobayashi, K., & Milner, J. (2013). Identification of the domains of cauliflower mosaic virus protein P6 responsible for suppression of RNA silencing and salicylic acid signalling. Journal of General Virology, 94(12), 2777-2789. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.057729-0
- Ubiquitination in plant nutrient utilizationYates, G., & Sadanandom, A. (2013). Ubiquitination in plant nutrient utilization. Frontiers in Plant Science, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00452
- Cauliflower mosaic virus protein P6 inhibits signaling responses to salicylic acid and regulates innate immunityLove, A., Geri, C., Laird, J., Carr, C., Yun, B., Loake, G., Tada, Y., Sadanandom, A., & Milner, J. (2012). Cauliflower mosaic virus protein P6 inhibits signaling responses to salicylic acid and regulates innate immunity. PLoS ONE, 7(10). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047535
- The ubiquitin-proteasome system: central modifier of plant signalling.Sadanandom, A., Bailey, M., Ewan, R., Lee, J., & Nelis, S. (2012). The ubiquitin-proteasome system: central modifier of plant signalling. New Phytologist, 196(1), 13-28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04266.x
- CMPG1-dependent cell death follows perception of diverse pathogen elicitors at the host plasma membrane and is suppressed by Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR3aGilroy, E., Taylor, R., Hein, I., Boevink, P., Sadanandom, A., & Birch, P. (2011). CMPG1-dependent cell death follows perception of diverse pathogen elicitors at the host plasma membrane and is suppressed by Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR3a. New Phytologist, 190(3), 653-666. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03643.x
- Deubiquitinating enzymes AtUBP12 and AtUBP13 and their tobacco homologue NtUBP12 are negative
regulators of plant immunityEwan, R., Pangestuti, R., Thornber, S., Craig, A., Carr, C., O’Donnell, L., Zhang, C., & Sadanandom, A. (2011). Deubiquitinating enzymes AtUBP12 and AtUBP13 and their tobacco homologue NtUBP12 are negativeregulators of plant immunity. New Phytologist, 191(1), 92-106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03672.x
- Biosensors in plantsSadanandom, A., & Napier, R. (2010). Biosensors in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 13(6), 736-743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2010.08.010
- Phytophthora infestans effector AVR3a is essential for virulence and manipulates plant immunity by stabilizing host E3 ligase CMPG1Bos, J., Armstrong, M., Gilroy, E., Boevink, P., Hein, I., Taylor, R., Tian, Z., Engelhardt, S., Vetukuri, R., Harrower, B., Dixelius, C., Bryan, G., Sadanandom, A., Whisson, S., Kamoun, S., & Birch, P. (2010). Phytophthora infestans effector AVR3a is essential for virulence and manipulates plant immunity by stabilizing host E3 ligase CMPG1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(21), 9909-9914. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914408107
- DAY NEUTRAL FLOWERING Represses CONSTANS to Prevent Arabidopsis Flowering Early in Short DaysMorris, K., Thornber, S., Codrai, L., Richardson, C., Craig, A., Sadanandom, A., Thomas, B., & Jackson, S. (2010). DAY NEUTRAL FLOWERING Represses CONSTANS to Prevent Arabidopsis Flowering Early in Short Days. Plant Cell, 22(4), 1118-1128. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.066605
- Genome sequence and analysis of the Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans.Haas, B., Kamoun, S., Zody, M., Jiang, R., Handsaker, R., Cano, L., Grabherr, M., Kodira, C., Raffaele, S., Torto-Alalibo, T., Bozkurt, T., Ah-Fong, A., Alvarado, L., Anderson, V., Armstrong, M., Avrova, A., Baxter, L., Beynon, J., Boevink, P., … Nusbaum, C. (2009). Genome sequence and analysis of the Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Nature, 461(7262), 393-398. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08358
- Response to Cacas and Diamond: Is the autophagy machinery an executioner of programmed cell death in plants?Love, A., Milner, J., & Sadanandom, A. (2009). Response to Cacas and Diamond: Is the autophagy machinery an executioner of programmed cell death in plants? Trends in Plant Science, 14(6), 300-301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.02.009
- E3 ubiquitin ligases and plant innate immunityCraig, A., Ewan, R., Mesmar, J., Gudipati, V., & Sadanandom, A. (2009). E3 ubiquitin ligases and plant innate immunity. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60(4), 1123-1132. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp059
- PrefaceSadanandom, A. (2009). Preface. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60(4), 1083-1083. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp064
- Towards understanding the virulence functions of RXLR effectors of the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora infestansBirch, P., Armstrong, M., Bos, J., Boevink, P., Gilroy, E., Taylor, R., Wawra, S., Pritchard, L., Conti, L., Ewan, R., Whisson, S., van West, P., Sadanandom, A., & Kamoun, S. (2009). Towards understanding the virulence functions of RXLR effectors of the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60(4), 1133-1140. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern353
- OTS1 and OTS2 SUMO proteases link plant development and survival under salt stressConti, L., Kioumourtzoglou, D., Donnell, E. O., Dominy, P., & Sadanandom, A. (2009). OTS1 and OTS2 SUMO proteases link plant development and survival under salt stress. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 4(3). https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.4.3.7867
- Timing is everything: regulatory overlap in plant cell deathLove, A., Milner, J., & Sadanandom, A. (2008). Timing is everything: regulatory overlap in plant cell death. Trends in Plant Science, 13(11), 589-595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.08.006
- Small Ubiquitin-Like Modifier Proteases OVERLY TOLERANT TO SALT1 and-2 Regulate Salt Stress Responses in ArabidopsisConti, L., Price, G., O’Donnell, E., Schwessinger, B., Dominy, P., & Sadanandom, A. (2008). Small Ubiquitin-Like Modifier Proteases OVERLY TOLERANT TO SALT1 and-2 Regulate Salt Stress Responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 20(10), 2894-2908. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058669
- An effector protein encoded by cauliflower mosaic virus inhibits SA-dependent defence responses in Arabidopsis via an NPR1-dependent mechanismLove, A., Geri, C., Laird, J., Yuri, B., Loake, G., Sadanandom, A., & Milner, J. (2008). An effector protein encoded by cauliflower mosaic virus inhibits SA-dependent defence responses in Arabidopsis via an NPR1-dependent mechanism. Comparative Biochemistry And Physiology A-Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 150(3), S193-S193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.04.528
- The cell death regulator AtPUB17 directly interacts with the BTB/POZ domain transcriptional repressor, AtBTB1 to control disease resistance in plantsSadanandom, A., Mesmar, J., Yang, C., Ewan, R., Carr, C., & O’ Donnell, E. (2008). The cell death regulator AtPUB17 directly interacts with the BTB/POZ domain transcriptional repressor, AtBTB1 to control disease resistance in plants. Comparative Biochemistry And Physiology A-Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 150(3), S178-S179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.04.475
- Cauliflower mosaic virus protein P6 is a suppressor of RNA silencingLove, A., Laird, J., Holt, J., Hamilton, A., Sadanandom, A., & Milner, J. (2007). Cauliflower mosaic virus protein P6 is a suppressor of RNA silencing. Journal of General Virology, 88, 3439-3444. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.83090-0
- The U-box protein AtPUB17 is a functional ortholog of NtACRE276 and its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity is required for plant cell death and defenceSadanandom, A. (2007). The U-box protein AtPUB17 is a functional ortholog of NtACRE276 and its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity is required for plant cell death and defence. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 146(4), S203-S203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.01.450
- SUMO proteases regulate ROS production in ArabidopsisConti, L., Donnel, E., Price, J., Love, A., Dominy, P., & Sadanandom, A. (2007). SUMO proteases regulate ROS production in Arabidopsis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 146(4), S260-S260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.01.656
- Role of SGT1 in resistance protein accumulation in plant immunityAzevedo, C., Betsuyaku, S., Peart, J., Takahashi, A., Noel, L., Sadanandom, A., Casais, C., Parker, J., & Shirasu, K. (2006). Role of SGT1 in resistance protein accumulation in plant immunity. EMBO Journal, 25(9), 2007-2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601084
- The E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of Arabidopsis PLANT U-BOX17 and its functional tobacco homolog ACRE276 are required for cell death and defenseYang, C., Gonzalez-Lamothe, R., Ewan, R., Rowland, O., Yoshioka, H., Shenton, M., Ye, H., O’Donnell, E., Jones, J., & Sadanandom, A. (2006). The E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of Arabidopsis PLANT U-BOX17 and its functional tobacco homolog ACRE276 are required for cell death and defense. Plant Cell, 18(4), 1084-1098. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.039198
- CHPA, a cysteine- and histidine-rich-domain-containing protein, contributes to maintenance of the diploid state in Aspergillus nidulansSadanandom, A., Findlay, K., Doonan, J., Schulze-Lefert, P., & Shirasu, K. (2004). CHPA, a cysteine- and histidine-rich-domain-containing protein, contributes to maintenance of the diploid state in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryotic Cell, 3(4), 984-991. https://doi.org/10.1128/ec.3.4.984-991.2004
- Ubiquitin ligase-associated protein SGT1 is required for host and nonhost disease resistance in plantsPeart, J., Lu, R., Sadanandom, A., Malcuit, I., Moffett, P., Brice, D., Schauser, L., Jaggard, D., Xiao, S., Coleman, M., Dow, M., Jones, J., Shirasu, K., & Baulcombe, D. (2002). Ubiquitin ligase-associated protein SGT1 is required for host and nonhost disease resistance in plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(16), 10865-10869. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.152330599
- Arabidopsis RAR1 exerts rate-limiting control of R gene-mediated defenses against multiple pathogensMuskett, P., Kahn, K., Austin, M., Moisan, L., Sadanandom, A., Shirasu, K., Jones, J., & Parker, J. (2002). Arabidopsis RAR1 exerts rate-limiting control of R gene-mediated defenses against multiple pathogens. Plant Cell, 14(5), 979-992. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.001040
- RAR1 and NDR1 contribute quantitatively to disease resistance in Arabidopsis, and their relative contributions are dependent on the R gene assayedTornero, P., Merritt, P., Sadanandom, A., Shirasu, K., Innes, R., & Dangl, J. (2002). RAR1 and NDR1 contribute quantitatively to disease resistance in Arabidopsis, and their relative contributions are dependent on the R gene assayed. Plant Cell, 14(5), 1005-1015. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.001032
- The RAR1 interactor SGT1, an essential component of R gene-triggered disease resistanceAzevedo, C., Sadanandom, A., Kitagawa, K., Freialdenhoven, A., Shirasu, K., & Schulze-Lefert, P. (2002). The RAR1 interactor SGT1, an essential component of R gene-triggered disease resistance. Science, 295(5562), 2073-2076.
- Differential regulation of plastidial and cytosolic isoforms of peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase in ArabidopsisSadanandom, A., Poghosyan, Z., Fairbairn, D., & Murphy, D. (2000). Differential regulation of plastidial and cytosolic isoforms of peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 123(1), 255-263.
- Identification of a peptide methionine sulphoxide reductase gene in an oleosin promoter from Brassica napusSadanandom, A., Piffanelli, P., Knott, T., Robinson, C., Sharpe, A., Lydiate, D., Murphy, D., & Fairbairn, D. (1996). Identification of a peptide methionine sulphoxide reductase gene in an oleosin promoter from Brassica napus. Plant Journal, 10(2), 235-242.

