Super-Resolution Microscopy
In optical microscopy, the resolution limit is defined by Abbe's principles. Generally this results in a lateral resolution (X-Y) limit of approximately 250nm and axial (Z) resolution of approximately 500nm.
Various optical techniques and sample preparation techniques result in this diffraction limit being broken. Durham's Biosciences Bioimaging facility are able to provide several super-resolution techniques which can be viewed below.
Super-Resolution Methods
Zeiss Airyscan
3D-SIM
Localisation Microscopy
Expansion Microscopy
GE Healthcare OMX V4.0
The system is an Applied Precision OMX BLAZE Super-Resolution microscope supplied by GE Healthcare.
The microscope can be utilised in several different modes;
- Widefield (conventional) mode
- 3D - SIM (Structured Illumination Microscopy)
- TIRF (Total Internal Reflection) mode
- Localisation microscopy - utilises images generated in TIRF mode
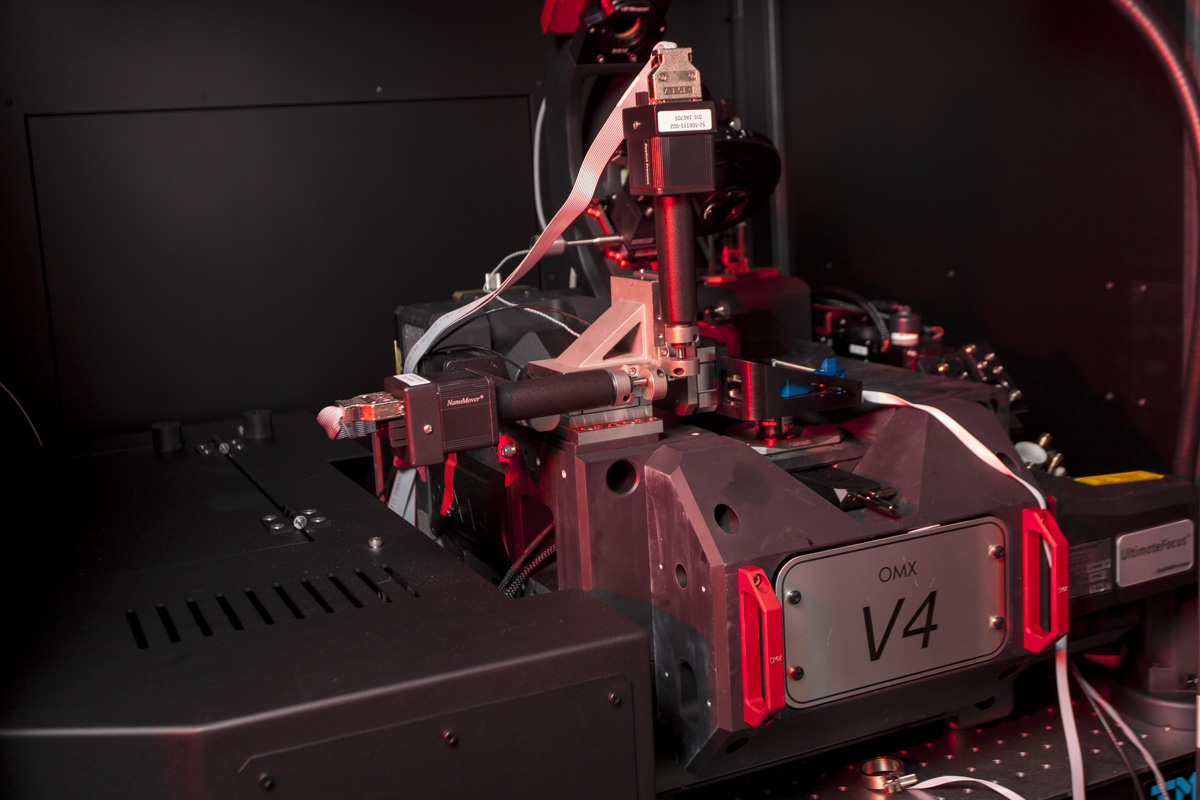
General Specification
Inverted microscope
Environmental control - temperature, humidity & CO2
Widefield (Conventional) Mode
The OMX can be used in its most simplest conventional mode to act as a very precise widefield microscope.
The fast camera speed of the OMX, dependent on camera exposure time, can run at approximately 40 fps
Ex 381-410nm/Em max. 436nm DAPI
Ex 461-493nm/Em max. 528nm FITC
Ex 562-581nm/Em max. 609nm A568
Ex 638-581nm/Em max. 683nm Cy5
Structured Illumination Specification
3D-SIM (Structured illumination Microscopy) which provides an 8 fold improvement in volumetric resolution (xy 100nm by z 250nm)
Solid state laser lines
405nm
445nm
488nm
514nm
568nm
642nm
TIRF Specification
Total Internal Reflection (TIRF) microscopy
The OMX utilises a novel Ring TIRF module - this rotates the laser beam rapidly at the back focal plane of the objective lens creating a highly uniform TIRF illumination.
TIRF mode is utilised for DeltaVision Localization Microscopy - capable of lateral resolution approximately 20-50nm
Objective Lenses
- 40 x oil - NA 1.3
- 60 x oil - NA 1.42
- 60 x silicone - NA 1.3
- TIRF 60 x - NA 1.49
- TIRF 100 x - NA 1.49


/prod01/prodbucket01/media/durham-university/departments-/biosciences/83453-1-1595X1594.jpg)
/prod01/prodbucket01/media/durham-university/departments-/biosciences/infrastructure-/bioimaging/Zeiss980_confocal.JPG)
/prod01/prodbucket01/media/durham-university/departments-/biosciences/infrastructure-/bioimaging/OMX.jpg)
/prod01/prodbucket01/media/durham-university/departments-/biosciences/infrastructure-/bioimaging/Expansion1.png)